Ever wondered what drives successful brands to dominate the market?
In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding marketing is crucial for businesses aiming to attract and retain loyal customers.
From traditional advertising methods to cutting-edge digital strategies, marketing encompasses a wide range of activities that help businesses connect with their target audience.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the core principles of marketing, including the famous 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.
We’ll delve into various types of marketing, such as social media, content, and influencer marketing, and explain the difference between inbound and outbound strategies.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or just starting, this guide will provide valuable insights to help you craft effective marketing campaigns that drive growth and success for your business.
Ready to dive into the world of marketing and discover strategies that can transform your business?
What is Marketing? Definition
Marketing is the strategic process of creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers through various methods. It involves market research, advertising, social media, content creation, and public relations to attract and retain customers. The goal of marketing is to understand consumer needs, build brand loyalty, and drive sales through effective campaigns.
Understanding Marketing
Marketing as a discipline involves a comprehensive set of actions designed to attract and retain customers while building lasting relationships. It begins with thorough market research to understand the target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors. By analyzing this data, businesses can create targeted strategies that effectively communicate their value propositions.
At its core, marketing seeks to match a company’s products or services with the needs of its customers. This involves crafting compelling messages, selecting the right communication channels, and ensuring that the product or service is accessible to the intended audience. Successful marketing not only drives sales but also fosters brand loyalty and customer engagement.
Marketing encompasses both traditional and digital methods. Traditional marketing includes print ads, billboards, and direct mail, while digital marketing leverages online platforms such as social media, email, and search engines. The integration of these methods allows marketers to reach customers wherever they are, creating a seamless and cohesive experience.
In addition to attracting new customers, marketing plays a crucial role in customer retention. Relationship marketing, for example, focuses on building long-term connections with customers through personalized communication and loyalty programs. This approach helps businesses maintain a loyal customer base and encourages repeat purchases.
Understanding marketing also means recognizing the importance of metrics and analytics. Marketers use various tools to measure the success of their campaigns, such as conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and return on marketing investment (ROMI). These insights enable continuous improvement and optimization of marketing strategies.
Marketing is a dynamic and multifaceted field that requires a deep understanding of consumer behavior, strategic planning, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. By mastering these elements, businesses can effectively promote their products and services, ultimately driving growth and success.
Purpose of Marketing
The primary purpose of marketing is to connect businesses with their target audience by creating, communicating, and delivering value. Marketing aims to understand consumer needs and desires, then develop strategies that satisfy those needs while achieving business objectives. Here are the key purposes of marketing:
- Customer Attraction and Acquisition: Marketing attracts potential customers by identifying their needs and presenting solutions that meet those needs. Through various strategies, such as advertising, content marketing, and social media, businesses can generate interest and drive traffic to their products or services.
- Building Brand Awareness: A strong marketing strategy helps establish and enhance brand awareness. By consistently communicating the brand’s value proposition across multiple channels, marketing ensures that consumers recognize and remember the brand. This builds trust and credibility, which are essential for long-term success.
- Customer Retention and Loyalty: Marketing isn’t just about acquiring new customers; it also focuses on retaining existing ones. Relationship marketing strategies, such as personalized communication and loyalty programs, help maintain a strong connection with customers, encouraging repeat purchases and fostering brand loyalty.
- Driving Sales and Revenue: Ultimately, marketing aims to drive sales and increase revenue. By effectively promoting products and services, marketing campaigns can influence purchasing decisions, convert leads into customers, and boost overall sales performance.
- Market Research and Insights: Marketing involves conducting market research to gather valuable insights about consumer behavior, preferences, and market trends. This information guides product development, pricing strategies, and promotional tactics, ensuring that the business remains competitive and relevant.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Marketing plays a crucial role in shaping the customer experience. By understanding and addressing customer pain points, marketers can create more satisfying and engaging interactions. This includes everything from user-friendly website design to responsive customer service.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective marketing differentiates a business from its competitors. By highlighting unique selling propositions (USPs) and leveraging innovative marketing tactics, businesses can stand out in a crowded marketplace and attract more customers.
What Are the 4 P’s of Marketing? (Marketing Mix)
The purpose of marketing is multifaceted, focusing on attracting and retaining customers, building brand awareness, driving sales, and gaining market insights. Through strategic planning and execution, marketing helps businesses achieve their goals and thrive in a competitive environment.
The 4 P’s of Marketing, also known as the marketing mix, are essential elements that guide the development and execution of marketing strategies. These elements—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—work together to ensure a product or service meets the needs of its target market and achieves business goals. Here’s a closer look at each of the 4 P’s:
- Product:
- Definition: A product is anything offered to a market to satisfy a want or need. It can be a physical good, a service, or even an idea.
- Key Considerations: Marketers must understand the product’s unique selling proposition (USP), features, benefits, and lifecycle. They also need to consider the design, quality, branding, and any variations or extensions.
- Example: A company selling a smartphone will focus on its features like camera quality, battery life, and unique functionalities that distinguish it from competitors.
- Price:
- Definition: Price is the amount of money customers must pay to acquire the product. It reflects the product’s perceived value and influences demand and profitability.
- Key Considerations: Pricing strategies can include penetration pricing, skimming, discount pricing, and competitive pricing. Factors like production costs, market conditions, and competitor pricing also play a role.
- Example: A luxury brand might use a premium pricing strategy to reinforce the perception of exclusivity and high quality.
- Place:
- Definition: Place refers to the distribution channels used to deliver the product to customers. It involves how and where the product is sold and the logistics behind getting it there.
- Key Considerations: Decisions include selecting retail locations, online platforms, distribution partners, and logistics. The goal is to make the product available in locations that are convenient for the target market.
- Example: An e-commerce business might focus on optimizing its website and partnering with reliable delivery services to ensure a seamless customer experience.
- Promotion:
- Definition: Promotion encompasses all the activities that communicate the product’s value and persuade customers to buy it. This includes advertising, sales promotions, public relations, and direct marketing.
- Key Considerations: Effective promotion strategies consider the target audience, messaging, timing, and budget. Marketers use various tools and channels to reach and engage potential customers.
- Example: A company launching a new product might use a mix of social media campaigns, email marketing, and influencer partnerships to generate buzz and drive sales.
By carefully balancing the 4 P’s, businesses can create effective marketing strategies that meet customer needs, enhance brand perception, and achieve business objectives. Each element must be thoughtfully integrated to support the overall marketing plan and deliver a cohesive and compelling value proposition to the market.
Types of Marketing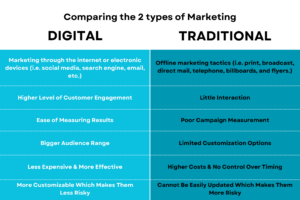
Marketing encompasses a broad range of strategies and channels to reach and engage customers. Below are various types of marketing, each with its unique approaches and benefits.
Internet Marketing
Internet marketing, also known as online marketing, involves promoting products or services over the internet. This broad category includes many other marketing types and strategies, from email to social media. It aims to reach potential customers through online channels where they spend a significant amount of time.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO is the process of optimizing a website to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This involves both on-page tactics, such as keyword optimization and content creation, and off-page tactics, such as link building. The goal is to increase organic traffic by making the site more visible to people searching for relevant terms.
Blog Marketing
Blog marketing involves creating and publishing articles on a website to attract and engage an audience. This content is typically informative or entertaining and is designed to provide value to readers. Blogs can help drive traffic, establish authority, and improve SEO by incorporating relevant keywords and attracting backlinks.
Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing uses platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and TikTok to connect with an audience. This can include organic posts, paid advertisements, and influencer partnerships. The aim is to increase brand awareness, engage with customers, and drive website traffic or sales.
Print Marketing
Print marketing involves advertising through physical media, such as newspapers, magazines, brochures, and billboards. Despite the digital shift, print marketing remains effective for reaching certain demographics and providing tangible promotional materials.
Search Engine Marketing (PPC)
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) involves paying for advertisements that appear on search engine results pages. The most common form is pay-per-click (PPC), where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. This method helps businesses quickly gain visibility and attract targeted traffic.
Video Marketing
Video marketing leverages video content to promote products or services. This can include commercials, explainer videos, product demonstrations, and customer testimonials. Platforms like YouTube and social media channels are commonly used for distributing video content.
Outdoor Marketing
Outdoor marketing, also known as out-of-home (OOH) advertising, involves physical advertisements in public spaces. This includes billboards, transit ads, posters, and any other large-scale print displays that reach consumers when they are outside their homes.
Direct Marketing
Direct marketing communicates directly with consumers to generate a response or transaction. This can include mailers, catalogs, telemarketing, and text messages. The focus is on targeting specific individuals with personalized messages and offers.
Electronic Marketing
Electronic marketing uses electronic media to advertise and sell products or services. This includes TV and radio commercials, as well as digital display ads on websites and mobile apps. It leverages audio-visual elements to capture attention and deliver compelling messages.
Event Marketing
Event marketing involves organizing or participating in events to promote a product, service, or brand. This can include trade shows, conferences, seminars, product launches, and sponsorships. Events provide opportunities for direct interaction with potential customers and partners.
Email Marketing
Email marketing uses email to send promotional messages, newsletters, and other types of communication to a list of subscribers. It is an effective way to nurture leads, build relationships, and drive conversions with personalized and targeted content.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing involves partnering with individuals or other companies (affiliates) to promote a product or service. Affiliates earn a commission for each sale or lead generated through their marketing efforts. This strategy expands reach and leverages the influence of affiliates.
Content Marketing
Content marketing focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience. The goal is to drive profitable customer action by providing information and solving problems for potential customers. This can include blogs, videos, infographics, eBooks, and more.
By leveraging these diverse types of marketing, businesses can reach their target audience through multiple channels, creating a cohesive and comprehensive marketing strategy that drives growth and success.
Marketing and Advertising
Marketing and advertising are closely related but distinct concepts within the broader field of promoting products or services. Understanding the difference between the two can help businesses craft more effective strategies to reach and engage their target audience.
Marketing
Marketing is a comprehensive process that encompasses all activities a company undertakes to promote and sell products or services. It involves understanding customer needs, developing products that meet those needs, creating compelling value propositions, and communicating them to the target audience. Marketing includes a variety of strategies and tactics, such as market research, branding, pricing, distribution, and customer relationship management.
Key components of marketing:
- Market Research: Gathering and analyzing data about consumer preferences, market trends, and competitive landscape to inform business decisions.
- Product Development: Designing and refining products or services based on market research and consumer feedback.
- Branding: Creating a unique identity and image for a product or company that differentiates it from competitors.
- Pricing Strategy: Setting prices based on production costs, competition, perceived value, and market demand.
- Distribution: Determining the best channels to deliver products to consumers, whether through physical stores, online platforms, or a combination.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Building and maintaining strong relationships with customers through personalized communication, loyalty programs, and excellent customer service.
Advertising
Advertising is a subset of marketing focused on promoting products or services through paid channels. It involves creating and delivering persuasive messages to a target audience with the goal of driving awareness, interest, and ultimately sales. Advertising can take many forms, including print ads, TV commercials, online banners, social media ads, and more.
Key aspects of advertising:
- Creating Ads: Developing creative and compelling advertisements that capture the attention of the target audience. This includes writing copy, designing visuals, and producing multimedia content.
- Media Planning and Buying: Selecting the right media channels (e.g., TV, radio, online) to reach the target audience effectively and negotiating the purchase of ad space or time.
- Targeting and Segmentation: Identifying specific segments of the market to focus advertising efforts on, ensuring that messages resonate with the right people.
- Campaign Execution: Implementing advertising campaigns across chosen media channels and monitoring their performance.
- Performance Measurement: Analyzing the effectiveness of advertising campaigns using metrics such as reach, impressions, click-through rates, and return on investment (ROI).
The Relationship Between Marketing and Advertising
Marketing and advertising are interconnected, with advertising being a crucial component of a broader marketing strategy. While marketing involves the overall strategy of understanding and meeting customer needs, advertising specifically focuses on communicating the value of products or services to potential customers through paid media.
For example, a company’s marketing strategy might include developing a new product based on consumer demand, setting a competitive price, and choosing the right distribution channels. Advertising then comes into play to create awareness and drive interest in the product through targeted campaigns on social media, TV, and other platforms.
By integrating marketing and advertising efforts, businesses can ensure that their promotional activities are aligned and mutually reinforcing, leading to a more effective approach to reaching and engaging their target audience.
Marketing Strategies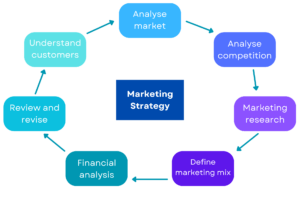
Marketing strategies are the overarching plans and approaches used by businesses to achieve their marketing goals. These strategies are designed to attract, engage, and convert customers, ultimately driving sales and business growth. Effective marketing strategies often blend traditional and digital methods to reach a wider audience.
Traditional Marketing Strategies
Traditional marketing strategies involve using conventional channels to promote products and services. These methods have been around for decades and are still effective in reaching certain audiences. Here are some key traditional marketing strategies:
- Print Marketing:
- Description: Utilizing newspapers, magazines, brochures, and direct mail to reach potential customers.
- Example: A local restaurant might use print ads in a community newspaper to attract nearby residents.
- Broadcast Marketing:
- Description: Advertising on television and radio to reach a broad audience.
- Example: A car dealership might run TV commercials during prime time to increase brand awareness and drive showroom traffic.
- Outdoor Marketing:
- Description: Placing advertisements in public spaces, such as billboards, transit ads, and posters.
- Example: A new fitness center might use billboard ads along busy highways to attract commuters.
- Direct Marketing:
- Description: Sending promotional materials directly to individuals through mail, telemarketing, or text messages.
- Example: A retail store might send out a catalog with special offers to its customer mailing list.
- Event Marketing:
- Description: Organizing or participating in events like trade shows, conferences, and product launches to engage with potential customers.
- Example: A technology company might host a booth at a tech expo to showcase its latest products.
Digital Marketing Strategies
Digital marketing strategies leverage online platforms and technologies to reach and engage customers. These methods have become increasingly important in the digital age, allowing businesses to target specific audiences with precision. Here are some key digital marketing strategies:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
- Description: Optimizing website content to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) and attract organic traffic.
- Example: A travel agency might use SEO to improve its visibility for search terms like “best vacation destinations.”
- Content Marketing:
- Description: Creating and distributing valuable content, such as blogs, videos, and infographics, to attract and engage a target audience.
- Example: A software company might publish a series of tutorials and case studies to demonstrate the benefits of its product.
- Social Media Marketing:
- Description: Using social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn to connect with customers and promote products.
- Example: A fashion brand might use Instagram to showcase new collections and interact with followers.
- Email Marketing:
- Description: Sending targeted email campaigns to nurture leads, build customer relationships, and drive sales.
- Example: An e-commerce site might send personalized product recommendations and discounts to its subscribers.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising:
- Description: Running paid ads on search engines, social media, and other websites where advertisers pay each time an ad is clicked.
- Example: An online retailer might use Google Ads to appear at the top of search results for keywords related to its products.
- Affiliate Marketing:
- Description: Partnering with individuals or other businesses (affiliates) who promote the product or service for a commission on sales generated.
- Example: A fitness supplement company might collaborate with fitness influencers who promote their products on their blogs and social media.
- Influencer Marketing:
- Description: Leveraging individuals with a large following to promote products to their audience.
- Example: A beauty brand might partner with a popular YouTuber to review and recommend its skincare line.
- Viral Marketing:
- Description: Creating content that is highly shareable and engaging, with the potential to go viral and reach a large audience quickly.
- Example: A fast-food chain might launch a quirky social media challenge that encourages users to participate and share.
- Video Marketing:
- Description: Using video content to engage audiences, explain products, and tell brand stories.
- Example: A tech company might create a series of product demonstration videos on YouTube.
- Event Marketing:
- Description: Hosting or participating in online events, webinars, and virtual conferences to connect with audiences.
- Example: A software company might host a webinar to demonstrate the latest features of its product and answer questions from attendees.
By combining traditional and digital marketing strategies, businesses can create a comprehensive marketing plan that reaches and engages their target audience through multiple channels, ultimately driving growth and success.
Inbound vs Outbound Marketing
Marketing strategies can be broadly categorized into two types: inbound marketing and outbound marketing. Each approach has distinct methods and goals, but both aim to attract and retain customers.
Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing focuses on attracting customers through valuable content and experiences tailored to them. It is about creating and sharing content that draws people to your business, rather than pushing your message out to them. The goal is to provide value and build trust, encouraging potential customers to seek out your products or services on their own terms.
Key Characteristics of Inbound Marketing:
- Content Creation: Producing high-quality, informative, and engaging content that addresses the needs and interests of your target audience. This includes blog posts, videos, eBooks, infographics, and more.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Optimizing your website and content to rank higher in search engine results, making it easier for potential customers to find you.
- Social Media Engagement: Building relationships with your audience on social media platforms through regular, meaningful interactions and content sharing.
- Email Marketing: Sending personalized, relevant emails to nurture leads and build ongoing relationships with customers.
- Lead Nurturing: Using automated workflows and targeted content to guide prospects through the buyer’s journey, from awareness to decision-making.
Examples of Inbound Marketing:
- A company publishes a series of blog posts addressing common customer pain points and solutions, driving organic traffic to its website.
- An eBook offered as a free download in exchange for a visitor’s email address, which is then used to send relevant follow-up content.
- A brand engaging with followers on social media, responding to comments and sharing user-generated content to build community and trust.
Outbound Marketing
Outbound marketing, also known as interruption or push marketing, involves actively reaching out to potential customers to get them interested in your products or services. This approach is more traditional and often uses paid advertising to broadcast a message to a wide audience, regardless of whether they have expressed interest.
Key Characteristics of Outbound Marketing:
- Advertising: Utilizing paid channels such as TV, radio, print ads, online display ads, and PPC (pay-per-click) campaigns to promote products and services.
- Cold Outreach: Contacting potential customers directly through methods like cold calling, direct mail, and unsolicited emails.
- Event Sponsorships: Participating in or sponsoring events to increase brand visibility and engage with attendees.
- Trade Shows and Exhibitions: Showcasing products or services at industry events to generate leads and build brand awareness.
- Public Relations: Gaining media coverage through press releases, interviews, and other PR activities to reach a broader audience.
Examples of Outbound Marketing:
- A company runs a TV commercial during prime time to reach a large, general audience.
- A retailer sends direct mail postcards with special offers to households in a specific geographic area.
- A business purchases a billboard ad along a busy highway to capture the attention of commuters.
- An online retailer uses PPC advertising to appear at the top of search engine results for specific keywords.
Comparing Inbound and Outbound Marketing
Approach:
- Inbound Marketing: Attracts customers by providing valuable content and engaging experiences that draw them in.
- Outbound Marketing: Pushes messages out to a wide audience to capture their attention and drive interest.
Cost:
- Inbound Marketing: Generally more cost-effective over time, as it focuses on organic growth and building long-term relationships.
- Outbound Marketing: Often requires a larger upfront investment for paid advertising and can be more expensive to maintain.
Engagement:
- Inbound Marketing: Encourages two-way communication and relationship-building with customers.
- Outbound Marketing: Typically one-way communication, with the brand broadcasting messages to potential customers.
Effectiveness:
- Inbound Marketing: Effective for building trust, generating leads, and nurturing long-term customer relationships.
- Outbound Marketing: Can quickly generate awareness and reach a large audience, but may be less effective for building lasting relationships.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both inbound and outbound marketing, businesses can create a balanced marketing strategy that leverages the best of both approaches. This ensures they can reach their target audience effectively and achieve their marketing goals.
Benefits of Marketing
Marketing is essential for the growth and success of any business. It encompasses a variety of strategies and tactics designed to attract, engage, and retain customers. Effective marketing can yield numerous benefits, from increased brand awareness to improved customer loyalty and higher sales. Here are some of the key benefits of marketing:
1. Increased Brand Awareness
- Description: Marketing helps build and enhance the visibility of your brand. By consistently communicating your brand’s value proposition through various channels, marketing ensures that more people recognize and remember your brand.
- Example: A comprehensive social media campaign can make your brand more recognizable and top-of-mind for potential customers.
2. Customer Acquisition
- Description: Effective marketing strategies attract new customers by identifying and targeting specific segments of the market. Through advertising, content marketing, and SEO, marketing brings in prospects who are interested in your products or services.
- Example: Running targeted Google Ads campaigns can drive traffic to your website and convert visitors into customers.
3. Customer Retention and Loyalty
- Description: Marketing is not just about acquiring new customers; it also focuses on retaining existing ones. Relationship marketing strategies, such as personalized communication and loyalty programs, help maintain a strong connection with customers, encouraging repeat business.
- Example: A loyalty program offering discounts and exclusive offers to returning customers can enhance customer retention.
4. Driving Sales and Revenue
- Description: The primary goal of marketing is to drive sales and increase revenue. By promoting products or services effectively, marketing campaigns can influence purchasing decisions and convert leads into customers.
- Example: Seasonal promotions and special offers can boost sales during key shopping periods.
5. Market Research and Insights
- Description: Marketing involves conducting market research to gather valuable insights about consumer behavior, preferences, and market trends. This information helps businesses make informed decisions about product development, pricing, and promotional strategies.
- Example: Surveys and focus groups can provide feedback on new product ideas before they are launched.
6. Enhanced Customer Experience
- Description: Marketing plays a crucial role in shaping the customer experience. By understanding and addressing customer pain points, marketers can create more satisfying and engaging interactions, leading to a better overall experience.
- Example: An intuitive website design and responsive customer service can significantly enhance the user experience.
7. Competitive Advantage
- Description: Effective marketing differentiates your business from competitors. By highlighting your unique selling propositions (USPs) and leveraging innovative marketing tactics, you can stand out in a crowded marketplace.
- Example: A brand that consistently delivers high-quality content and engages with its audience on social media can build a strong competitive edge.
8. Building Brand Loyalty
- Description: Marketing helps in creating and nurturing brand loyalty by consistently delivering value and maintaining strong relationships with customers. Loyal customers are more likely to make repeat purchases and recommend your brand to others.
- Example: A company that engages with its customers through personalized email campaigns and social media interactions can build a loyal customer base.
9. Long-term Growth
- Description: Sustainable marketing strategies contribute to the long-term growth of a business. By continuously attracting new customers and retaining existing ones, marketing ensures steady revenue streams and business expansion.
- Example: A well-planned content marketing strategy can drive continuous traffic and generate leads over time.
10. Improved Return on Investment (ROI)
- Description: By using data-driven strategies and measuring the performance of marketing campaigns, businesses can optimize their marketing spend and achieve a higher ROI. This involves analyzing metrics such as conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and lifetime value.
- Example: A/B testing different ad creatives can help identify the most effective approach, maximizing the return on advertising spend.
In summary, marketing offers a wide range of benefits that are crucial for the success and growth of any business. From increasing brand awareness and driving sales to enhancing customer loyalty and gaining valuable market insights, effective marketing strategies help businesses achieve their objectives and thrive in a competitive environment.
Limitations of Marketing
While marketing is essential for business success, it is not without its limitations. Understanding these limitations helps businesses navigate challenges and develop more effective strategies. Here are some key limitations of marketing:
1. High Costs
- Description: Effective marketing campaigns often require significant financial investment, including costs for advertising, content creation, and market research. Small businesses with limited budgets may struggle to compete with larger companies.
- Example: Running a comprehensive PPC campaign across multiple platforms can quickly become expensive, especially in highly competitive industries.
2. Measurability Challenges
- Description: Although digital marketing offers advanced analytics tools, accurately measuring the return on investment (ROI) for certain marketing activities can still be challenging. Attribution, or determining which marketing efforts lead to conversions, can be complex.
- Example: Multi-channel campaigns make it difficult to pinpoint whether a sale was driven by a social media post, an email, or a combination of both.
3. Market Saturation
- Description: In markets with high competition, it can be difficult for businesses to differentiate themselves and capture the attention of their target audience. Consumers are often bombarded with marketing messages, leading to advertising fatigue.
- Example: In the fashion industry, countless brands compete for attention, making it hard for new entrants to stand out.
4. Consumer Skepticism
- Description: Increasing awareness of marketing tactics has made consumers more skeptical and critical of advertising messages. Trust is harder to build, and customers may doubt the authenticity of marketing claims.
- Example: Consumers may be wary of influencer endorsements if they believe the influencer is motivated solely by financial gain rather than genuine appreciation of the product.
5. Rapid Technological Changes
- Description: The marketing landscape is continuously evolving with new technologies, platforms, and trends. Keeping up with these changes requires ongoing learning and adaptation, which can be resource-intensive.
- Example: The rise of new social media platforms like TikTok requires marketers to quickly develop expertise and strategies for these channels.
6. Short-Term Focus
- Description: Some marketing strategies, particularly those driven by immediate sales goals, may neglect long-term brand building and customer relationships. Overemphasis on short-term results can undermine sustainable growth.
- Example: Aggressive discounting strategies can boost short-term sales but may damage the brand’s premium image and erode profit margins.
7. Legal and Ethical Issues
- Description: Marketing activities must comply with various laws and regulations, including data privacy laws, advertising standards, and consumer protection laws. Ethical considerations also play a crucial role in maintaining brand reputation.
- Example: Non-compliance with GDPR can result in hefty fines and damage to brand reputation for businesses operating in the European Union.
8. Dependence on External Factors
- Description: Marketing success can be heavily influenced by external factors beyond a business’s control, such as economic conditions, political climate, and social trends. These factors can impact consumer behavior and market dynamics.
- Example: Economic downturns can reduce consumers’ purchasing power, leading to lower sales despite effective marketing efforts.
9. Creative Limitations
- Description: Despite the need for creativity in marketing, there can be limitations due to budget constraints, brand guidelines, and regulatory requirements. These restrictions can stifle innovation and creative freedom.
- Example: Pharmaceutical companies face strict advertising regulations that limit the ways they can promote their products, often leading to less creative marketing approaches.
10. Consumer Bias
- Description: Existing customer biases and preferences can make it difficult for new products or brands to gain traction. Consumers often stick to familiar brands and may resist switching to new offerings.
- Example: A new soft drink brand may struggle to convince loyal Coca-Cola or Pepsi drinkers to try its product, despite innovative marketing campaigns.
Understanding these limitations allows businesses to anticipate challenges and develop strategies to mitigate their impact. By recognizing and addressing these constraints, marketers can create more resilient and adaptable marketing plans that better support long-term business objectives.
Relationship Marketing
Relationship marketing focuses on building long-term relationships with customers rather than just aiming for short-term sales. This strategy emphasizes customer satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement through personalized communication, excellent customer service, and loyalty programs. By fostering strong connections, businesses can enhance customer retention and encourage repeat purchases.
Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing leverages individuals with significant followings on social media or other platforms to promote products or services. Brands collaborate with influencers who can reach and persuade their target audience through authentic and relatable content. This method helps increase brand awareness and credibility, especially among niche markets.
Viral Marketing
Viral marketing aims to create highly shareable content that spreads quickly and widely across the internet, much like a virus. This strategy relies on the audience to share the content organically, leading to exponential growth in visibility. Successful viral marketing campaigns often include memorable, entertaining, or emotionally resonant elements that encourage sharing.
Guerilla Marketing
Guerilla marketing uses unconventional, creative, and often low-cost tactics to capture attention and generate buzz. This approach typically involves surprising or engaging the audience in unexpected ways to make a lasting impression. Examples include flash mobs, street art, and pop-up events. Guerilla marketing is effective for creating strong, memorable brand experiences.
Green Marketing
Green marketing, also known as environmental or eco-marketing, promotes products or services based on their environmental benefits. This strategy highlights sustainable practices, eco-friendly materials, and corporate social responsibility. By appealing to environmentally conscious consumers, businesses can differentiate themselves and build a positive brand image focused on sustainability.
Data and Analytics for Marketers
Data and analytics play a crucial role in modern marketing by providing insights that drive decision-making and strategy. Marketers use various tools to collect and analyze data on consumer behavior, campaign performance, and market trends. Key metrics include website traffic, conversion rates, customer demographics, and engagement levels. By leveraging data, marketers can optimize their campaigns, personalize customer experiences, and measure the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
How Success is Measured in Marketing
Marketing success is measured using a variety of metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics help marketers evaluate the effectiveness of their campaigns and strategies. Common metrics include:
-
- Total Revenue: The overall income generated from marketing activities.
- Profit: The overall profit after expenses
- Sales Growth: The increase in sales over a specific period.
- Customer Loyalty: Metrics like Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) and repeat purchase rates.
- Return on Marketing Investment (ROMI): Revenue generated divided by the marketing spend.
- Conversion Rates: The percentage of users who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. By tracking these metrics, businesses can assess the impact of their marketing efforts and make data-driven decisions.
Why Is Marketing So Important?
Marketing is essential for the success and growth of any business. It helps in building brand awareness, attracting new customers, and retaining existing ones. Effective marketing communicates the value of a product or service, differentiates it from competitors, and drives sales. Additionally, marketing provides insights into consumer behavior and market trends, guiding product development and strategic planning. In essence, marketing connects businesses with their audience, fostering relationships that lead to sustained growth and profitability.
Final Thoughts: What is Marketing
Marketing is a multifaceted discipline that plays a vital role in the success of any business. From understanding customer needs to crafting compelling messages and leveraging various channels, effective marketing strategies can drive growth, enhance brand loyalty, and improve customer satisfaction. While it comes with challenges and limitations, the benefits of well-executed marketing are substantial. By continually adapting to changing market conditions and utilizing data-driven insights, businesses can ensure their marketing efforts remain impactful and relevant. Whether through traditional methods or digital innovations, the core principles of marketing remain focused on delivering value and building lasting relationships with customers.
FAQ
Is marketing the same as advertising? No, marketing and advertising are not the same. Marketing is a broad discipline that involves research, strategy, and various tactics to understand and meet customer needs. Advertising is a subset of marketing focused on promoting products or services through paid channels to reach a targeted audience.
How are marketing and branding different? Marketing involves the activities and strategies used to promote products or services and engage customers. Branding, on the other hand, is about creating a unique identity and image for a product or company. Branding includes elements like logos, design, and messaging, which help shape consumers’ perceptions and create emotional connections with the brand.
What’s the difference between marketing and sales? Marketing focuses on creating awareness, interest, and demand for products or services through various strategies and campaigns. Sales involve directly interacting with potential customers to persuade them to purchase. While marketing generates leads and builds a foundation for customer interest, sales convert those leads into actual customers.
What are the 4 principles of marketing? The 4 principles of marketing, also known as the 4 P’s, are:
- Product: The goods or services offered to meet customer needs.
- Price: The amount charged for the product.
- Place: The distribution channels used to deliver the product to customers.
- Promotion: The methods used to communicate and persuade customers to purchase the product.
What is the definition of marketing? Marketing is the strategic process of creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers through various methods. It involves market research, advertising, social media, content creation, and public relations to attract and retain customers. The goal of marketing is to understand consumer needs, build brand loyalty, and drive sales through effective campaigns.
What is the real meaning of marketing? The real meaning of marketing is the process of identifying and meeting the needs and desires of customers through value creation and exchange. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including product development, pricing strategy, distribution, and promotion, all aimed at satisfying customer demands and achieving business goals.
What is the concept of marketing? The concept of marketing centers on understanding and satisfying customer needs and wants. It involves a customer-oriented approach, where businesses focus on creating products and services that provide value to their target audience. This concept emphasizes the importance of market research, customer feedback, and continuous improvement to stay relevant and competitive.
What is marketing and why is it important? Marketing is the process of creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers. It is important because it helps businesses connect with their target audience, build brand awareness, and drive sales. Effective marketing strategies attract new customers, retain existing ones, and provide valuable insights into market trends and consumer behavior, ultimately leading to business growth and success.

